Introduction to BARD Transactions
- Understanding the basics of BARD transactions
- Importance of transaction knowledge for investors and users
- Overview of BARD transaction characteristics and benefits
BARD transactions represent the fundamental way value is transferred within the decentralized network of this digital asset. Unlike traditional financial transactions that rely on intermediaries and centralized authorities, BARD transactions operate on a peer-to-peer basis secured by cryptographic verification. Each BARD transaction is recorded on the BARD distributed ledger, making it transparent and immutable.
For investors, traders, and everyday users of BARD, understanding how BARD transactions work is crucial for ensuring funds are transferred securely, optimizing for lower fees, and troubleshooting any issues that might arise. Whether you're sending BARD tokens to another wallet, trading BARD on an exchange, or interacting with decentralized applications, transaction knowledge serves as your foundation for effective BARD management.
BARD transactions offer several distinctive advantages, including settlement times as quick as a few seconds to minutes without intermediaries, the ability to send value globally without permission from financial institutions, and programmable transfer logic through smart contracts. However, they also require users to understand the irreversible nature of BARD blockchain transactions and take responsibility for proper address verification before sending.
How BARD Transactions Work: Technical Fundamentals
- Blockchain foundation supporting BARD transactions
- Transaction verification and consensus mechanism
- Public and private keys in transaction security
- Transaction fees structure and purpose
At its core, BARD operates on a blockchain where BARD transactions are bundled into blocks and cryptographically linked to form an unbroken chain of records. When you initiate a BARD transaction, it gets verified by network validators who confirm that you actually own the BARD tokens you're attempting to send by checking your digital signature against your public key.
The consensus mechanism ensures that all BARD network participants agree on the valid state of transactions, preventing issues like double-spending where someone might attempt to send the same BARD tokens to different recipients. In BARD's network, this consensus is achieved through validator selection and cryptographic proofs, requiring BARD token holdings and computational resources to secure the network.
Your BARD wallet manages a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key that must be kept secure at all times, and a public key from which your BARD wallet address is derived. When sending BARD, your wallet creates a digital signature using your private key, proving ownership without revealing the key itself – similar to signing a check without revealing your signature pattern.
Transaction fees for BARD are determined by network congestion, transaction size/complexity, and priority level requested by the sender. These BARD fees serve to compensate validators for their work, prevent spam attacks on the network, and prioritize transactions during high demand periods. The BARD fee structure works by specifying gas price and limits depending on the network design.
Step-by-Step BARD Transaction Process
- Creating a transaction request
- Transaction signing and authorization
- Broadcasting the transaction to the network
- Confirmation process and verification
- Tracking your transaction status
The BARD transaction process can be broken down into these essential steps:
Step 1: Prepare Transaction Details
- Specify the recipient's BARD address format (alphanumeric string, typically starting with a specific prefix)
- Determine the exact amount of BARD to send
- Set an appropriate BARD transaction fee based on current network conditions
- Most BARD wallets provide fee estimation tools to balance cost and confirmation speed
Step 2: Sign the Transaction
- Your BARD wallet constructs a digital message containing sender address, recipient address, amount, and fee information
- This message is cryptographically signed using your private key
- The signing process creates a unique signature that proves you authorized the BARD transaction
- This entire process happens locally on your device, keeping your private keys secure
Step 3: Broadcast to Network
- Your wallet broadcasts the signed BARD transaction to multiple nodes in the BARD network
- These nodes verify the transaction's format and signature
- Verified BARD transactions are relayed to other connected nodes
- Within seconds, your BARD transaction propagates across the entire network
- Your transaction now sits in the memory pool (mempool) awaiting inclusion in a block
Step 4: Confirmation Process
- BARD validators select transactions from the mempool, prioritizing those with higher fees
- Once included in a block and added to the blockchain, your BARD transaction receives its first confirmation
- Each subsequent block represents an additional confirmation
- Most services consider a BARD transaction fully settled after 3-6 confirmations
Step 5: Verification and Tracking
- Track your BARD transaction status using blockchain explorers by searching for your transaction hash (TXID)
- These explorers display confirmation count, block inclusion details, fee paid, and exact timestamp
- For BARD, popular explorers include MEXC's integrated explorer and other BARD ecosystem-specific tools
- Once fully confirmed, the recipient can safely access and use the transferred BARD funds
Transaction Speed and Fees Optimization
- Factors affecting BARD transaction speed
- Understanding fee structures and calculation methods
- Tips for reducing transaction costs
- Network congestion impacts and planning transactions
BARD transaction speeds are influenced by network congestion, fee amount you're willing to pay, and the blockchain's inherent processing capacity. During periods of high network activity, such as major market movements or protocol upgrades, completion times can increase from the usual few seconds to minutes to longer periods unless higher BARD transaction fees are paid.
The fee structure for BARD is based on a gas-like mechanism. Each BARD transaction requires computational resources to process, and fees are essentially bids for inclusion in the next block. The minimum viable BARD fee changes constantly based on network demand, with wallets typically offering fee tiers such as economy, standard, and priority to match your urgency needs.
To optimize BARD transaction costs while maintaining reasonable confirmation times, consider:
- Transacting during off-peak hours when BARD network activity naturally decreases, typically weekends or between 02:00–08:00 UTC
- Batching multiple operations into a single BARD transaction when the protocol allows
- Utilizing layer-2 solutions or sidechains for frequent small BARD transfers (if supported)
- Subscribing to fee alert services that notify you when BARD network fees drop below your specified threshold
Network congestion impacts BARD transaction times and costs significantly, with BARD's block time of approximately 10 seconds serving as the minimum possible confirmation time. During major market volatility events, the mempool can become backlogged with thousands of pending BARD transactions, creating a competitive fee market where only transactions with premium fees get processed quickly. Planning non-urgent BARD transactions for historical low-activity periods can result in fee savings of 30% or more compared to peak times.
Common Transaction Issues and Solutions
- Troubleshooting stuck or pending transactions
- Addressing failed transactions
- Double-spending prevention
- Verification of recipient addresses
- Security best practices for safe transactions
Stuck or pending BARD transactions typically occur when the fee set is too low relative to current network demand, there are nonce sequence issues with the sending wallet, or network congestion is extraordinarily high. If your BARD transaction has been unconfirmed for more than 1–2 hours, you can attempt a fee bump/replace-by-fee if the protocol supports it, use a transaction accelerator service, or simply wait until BARD network congestion decreases as most transactions eventually confirm or get dropped from the mempool after 24–48 hours.
Failed BARD transactions can result from insufficient funds to cover both the sending amount and transaction fee, attempting to interact with BARD smart contracts incorrectly, or reaching network timeout limits. The most common error messages include "insufficient balance", "invalid nonce", and "out of gas", each requiring different remediation steps. Always ensure your BARD wallet contains a buffer amount beyond your intended transaction to cover unexpected fee increases during processing.
BARD's blockchain prevents double-spending through its consensus protocol, but you should still take precautions like waiting for the recommended number of confirmations before considering large BARD transfers complete, especially for high-value transactions. The BARD protocol's design makes transaction reversal impossible once confirmed, highlighting the importance of verification before sending.
Address verification is critical before sending any BARD transaction. Always double-check the entire BARD recipient address, not just the first and last few characters. Consider sending a small test amount of BARD before large transfers, using the QR code scanning feature when available to prevent manual entry errors, and confirming BARD addresses through a secondary communication channel when sending to new recipients. Remember that BARD blockchain transactions are generally irreversible, and funds sent to an incorrect address are typically unrecoverable.
Security best practices include using hardware wallets for significant BARD holdings, enabling multi-factor authentication on exchange accounts, verifying all BARD transaction details on your wallet's secure display, and being extremely cautious of any unexpected requests to send BARD. Be aware of common scams like phishing attempts claiming to verify your BARD wallet, fake support staff offering BARD transaction help in direct messages, and requests to send BARD tokens to receive a larger amount back.
Conclusion
Understanding the BARD transaction process empowers you to confidently navigate the BARD ecosystem, troubleshoot potential issues before they become problems, and optimize your usage for both security and efficiency. From the initial creation of a BARD transaction request to final confirmation on the blockchain, each step follows logical, cryptographically-secured protocols designed to ensure trustless, permissionless value transfer. As BARD continues to evolve, transaction processes will likely see greater scalability through protocol upgrades, reduced BARD fees via network optimizations, and enhanced privacy features. Staying informed about these BARD developments through official documentation, community forums, and reputable news sources will help you adapt your transaction strategies accordingly and make the most of this innovative digital asset.
Mô tả: Nhịp đập tiền mã hoá áp dụng AI và các nguồn công khai để nhanh chóng mang đến những xu hướng token hot nhất. Để xem nhận định từ chuyên gia và phân tích chuyên sâu, vui lòng truy cập MEXC Learn.
Các bài viết được chia sẻ trên trang này được lấy từ các nền tảng công khai và chỉ nhằm mục đích tham khảo. Các bài viết này không nhất thiết đại diện cho quan điểm của MEXC. Mọi quyền sở hữu thuộc về tác giả gốc. Nếu bạn cho rằng bất kỳ nội dung nào vi phạm quyền của bên thứ ba, vui lòng liên hệ service@support.mexc.com để được xử lý kịp thời.
MEXC không đảm bảo tính chính xác, đầy đủ hoặc kịp thời của bất kỳ nội dung nào và không chịu trách nhiệm cho các hành động được thực hiện dựa trên thông tin cung cấp. Nội dung này không cấu thành lời khuyên tài chính, pháp lý hoặc chuyên môn khác, và cũng không được xem là khuyến nghị hoặc xác nhận từ MEXC.
Cập nhật mới nhất về Lombard
Xem thêm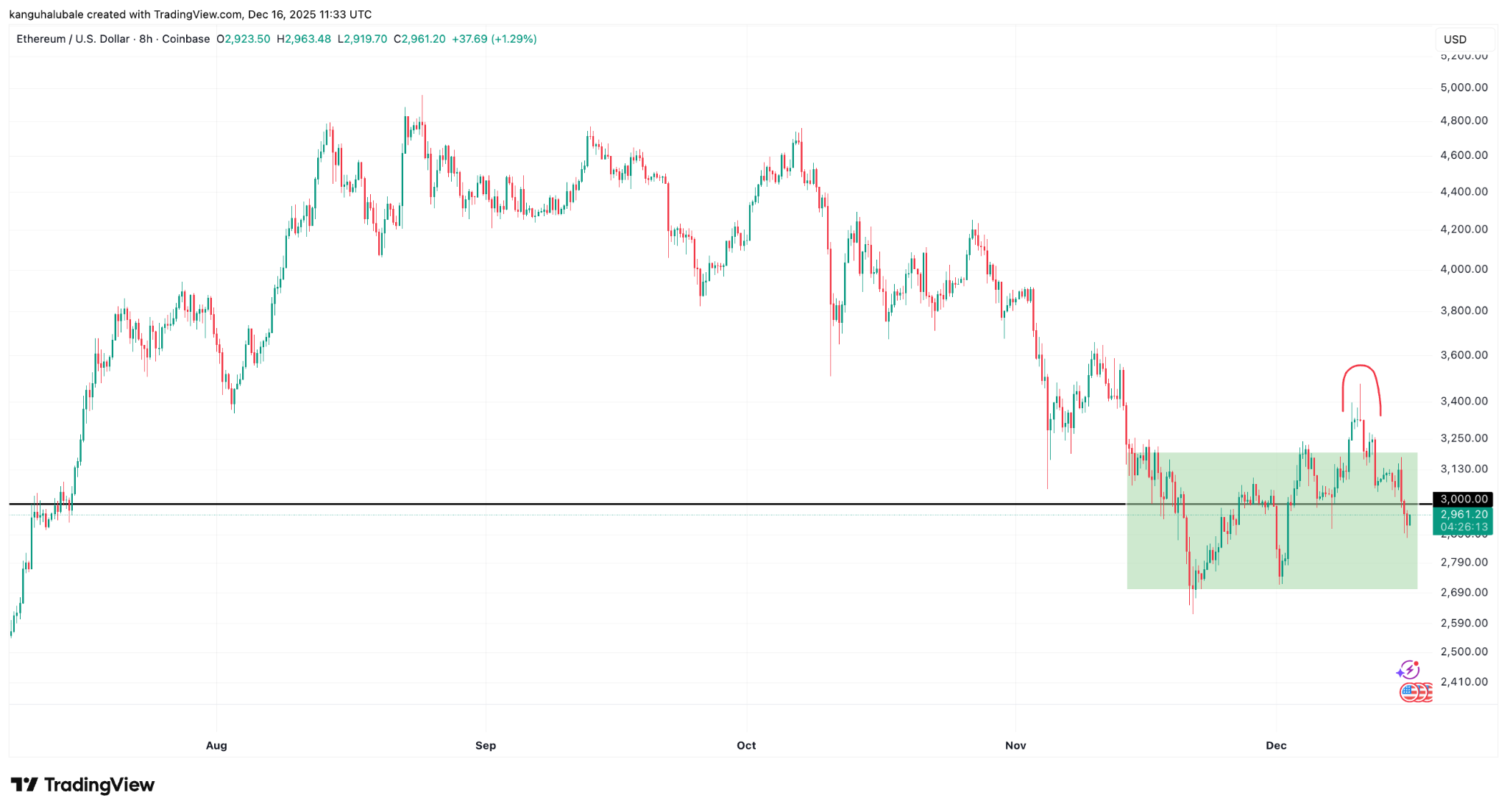
Tại sao Ether không thể giữ được mức 3.000 đô la? Khả năng phục hồi đang bị nghi ngờ

Cổ phiếu HashKey giảm 5% ngày chào sàn Hồng Kông
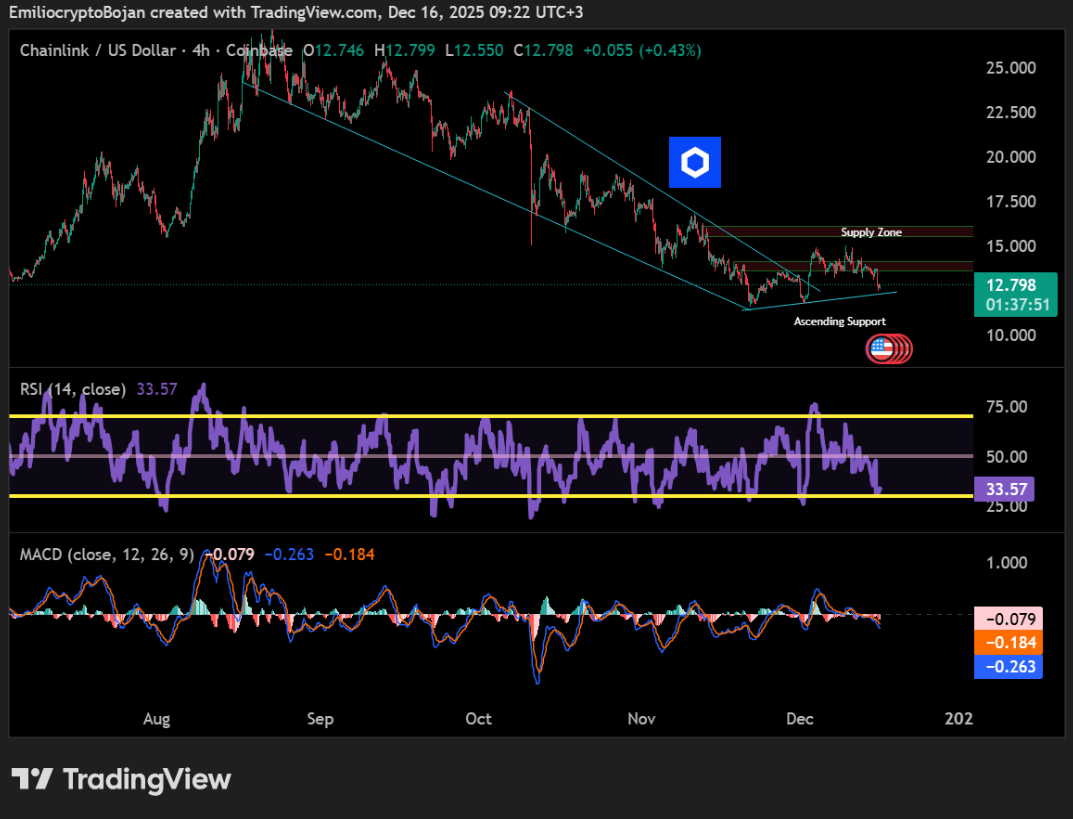
Giá Chainlink chững lại – Nhưng đây là lý do tại sao nhà đầu tư thông minh vẫn tiếp tục rót vốn vào
HOT
Tiền mã hoá thịnh hành hiện nay đang thu hút sự chú ý đáng kể của thị trường
Giá tiền mã hoá
Tiền mã hoá có khối lượng giao dịch cao nhất
Mới được thêm vào
Tiền mã hoá được niêm yết gần đây có thể giao dịch
