A Simpler Formula for Curve Approximation Using Arc Segments
Table Of Links
ABSTRACT
1 INTRODUCTION
2 FLATTENING AND ARC APPROXIMATION OF CURVES
3 EULER SPIRALS AND THEIR PARALLEL CURVES
4 FLATTENED PARALLEL CURVES
5 ERROR METRICS FOR APPROXIMATION BY ARCS
6 EVOLUTES
7 CONVERSION FROM CUBIC BÉZIERS TO EULER SPIRALS
8 GPU IMPLEMENTATION
9 RESULTS
CONCLUSIONS, FUTURE WORK AND REFERENCES
\
ERROR METRICS FOR APPROXIMATION BY ARCS
The problem of approximating a curve by a sequence of arc segments has extensive literature, but none of the published solutions are quite suitable for our application. The specific problem of approximating an Euler spiral by arcs is considered in Meek and Walton [2004] using a “cut then measure” adaptive subdivision scheme, but their solution has poor quality; it scales as 𝑂(1/𝑛 2 ), while 𝑂(1/𝑛 3 ) is attainable. The result was improved “slightly” by Narayan [2014].
\ The literature also contains optimal results, namely Maier [2014] and Nuntawisuttiwong and Dejdumrong [2021], but at considerable cost; both approaches claim 𝑂(𝑛 2 ) time complexity. The through-line for all these results is that they are solving a harder problem: adopting the constraint that the generated arc sequence is 𝐺 1 continuous. While desirable for many applications, this constraint is not needed for rendering a stroke outline.
\ Even with this constraint relaxed, the angle discontinuities of an arc approximation are tiny compared to flattening to lines. Our approach is based on a simple error metric, similar in flavor to the one for flattening to line segments. The details of the metric (in particular, tuning of constants) were obtained empirically, though we suspect that more rigorous analytic bounds could be obtained. In practice it works very well indeed; the best way to observe that is an interactive testing tool, which is provided in the supplemental materials.
The proposed error metric is as follows. The estimated distance error for a curve of length 𝑠ˆ is:
𝑑 ≈ 1 120 ∫ 𝑠ˆ 0 3 √︁ |𝜅 ′ (𝑠)|𝑑𝑠!3
For an Euler spiral segment, 𝜅 ′ (𝑠) is constant and thus this error metric becomes nearly trivial. With 𝑛 subdivisions, the estimated distance is simply 𝑠 3𝜅 ′ 120𝑛 3 . Solving for 𝑛, we get 𝑛 = 𝑠 3 √︃ |𝜅 ′ | 120𝑑 subdivisions, and those are divided evenly by arc length, as the subdivision density is constant across the curve, just as is the case for flattening arcs to lines. Remarkably, the approximation of an Euler spiral parallel curve by arc segments is almost as simple as that for Euler spirals to arcs.
\ As in flattening to lines, the parameter for the curve is the arc length of the originating Euler spiral. The subdivision density is then constant, and only a small tweak is needed to the formula for computing the number of subdivisions, taking into account the additional curvature variation from the offset by ℎ (the half line-width). The revised formula is:
𝑛 = 𝑠 3 √︂ |𝜅 ′ | (1 + 0.4|ℎ𝑠𝜅′ |) 120𝑑
This formula was determined empirically by curve-fitting measured error values from approximating Euler spiral parallel curves to arcs, but was also inspired by applying the general error metric formula to the analytical equations for Euler spiral parallel curve, and dropping higher order terms. A more rigorous derivation, ideally with firm error bounds, remains as future work.
\ One consequence of this formula is that, since the error is in terms of the absolute value of ℎ, independent of sign, the same arc approximation can be used for both sides of a stroke. See Figure 8 for a comparison between flattening to a polyline and approximation with arc segments. The arc segment version has many fewer segments at the same tolerance, while preserving very high visual quality.
EVOLUTES
In the principled, correct specification for stroking [19], parallel curves are sufficient only for segments in which the curvature
\ 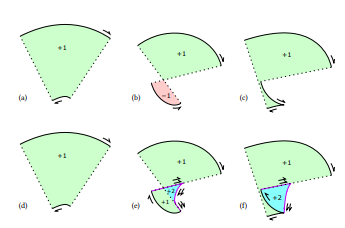
\ does not exceed the reciprocal half-width. When it does, additional segments must be drawn, including evolutes of the original curve. In general, the evolute of a cubic Bézier is a very complex curve, requiring approximation techniques. By contrast, the evolute of an Euler spiral (𝜅 = 𝑎𝑠) is another spiral with a simple Cesàro equation, namely 𝜅 = −𝑎 −1 𝑠 −3 , an instance of the general result that the evolute of a log-aesthetic curve is another log-aesthetic curve [26].
\ Flattening this evolute is also straightforward; the subdivision density is proportional to 𝑠 −0.5 where 𝑠 is the arc length parameter of the underlying Euler spiral (and translated so 𝑠 = 0 is the inflection point). Thus, the integral is 2 √ 𝑠, and the inverse integral is just squaring. Thus, flattening the evolute of an Euler spiral is simpler than flattening its parallel curve. T
\ he effect of adding evolutes to achieve strong correctness is shown in Figure 9. The additional evolute segments and connecting lines are output twice, to make the winding numbers consistent and produce a watertight outline. All winding numbers are positive, so rendering with the nonzero winding rule yields a correct final render.
:::info Authors:
- Raph Levien
- Arman Uguray
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.
:::
\
You May Also Like
XRP Bulls Gain Confidence as Social Sentiment Turns Positive

The HackerNoon Newsletter: Cypherpunks Write Code: Zooko Wilcox Zcash (9/21/2025)
![[Two Pronged] Has my fate made me end up with the same type of woman every time?](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2025/12/two-pronged-2-Factor-Authentication-relationship.jpg)