Streamline Structured + Unstructured Data Flows from Postgres with AI
CocoIndex is one framework for building incremental data flows across structured and unstructured sources.
In CocoIndex, AI steps -- like generating embeddings -- are just transforms in the same flow as your other types of transformations, e.g. data mappings, calculations, etc. ==⭐ Star CocoIndex on GitHub and share the love :heart:!==
Why One Framework for Structured + Unstructured?
- One mental model: Treat files, APIs, and databases uniformly; AI steps are ordinary ops.
- Incremental by default: Use an ordinal column to sync only changes; no fragile glue jobs.
- Consistency: Embeddings are always derived from the exact transformed row state.
- Operational simplicity: One deployment, one lineage view, fewer moving parts.
This blog introduces the new PostgreSQL source and shows how to take data from PostgreSQL table as source, transform with both AI models and non-AI calculations, and write them into a new PostgreSQL table for semantic + structured search.
If this helps you, ⭐ Star CocoIndex GitHub!
The Example: PostgreSQL Product Indexing Flow
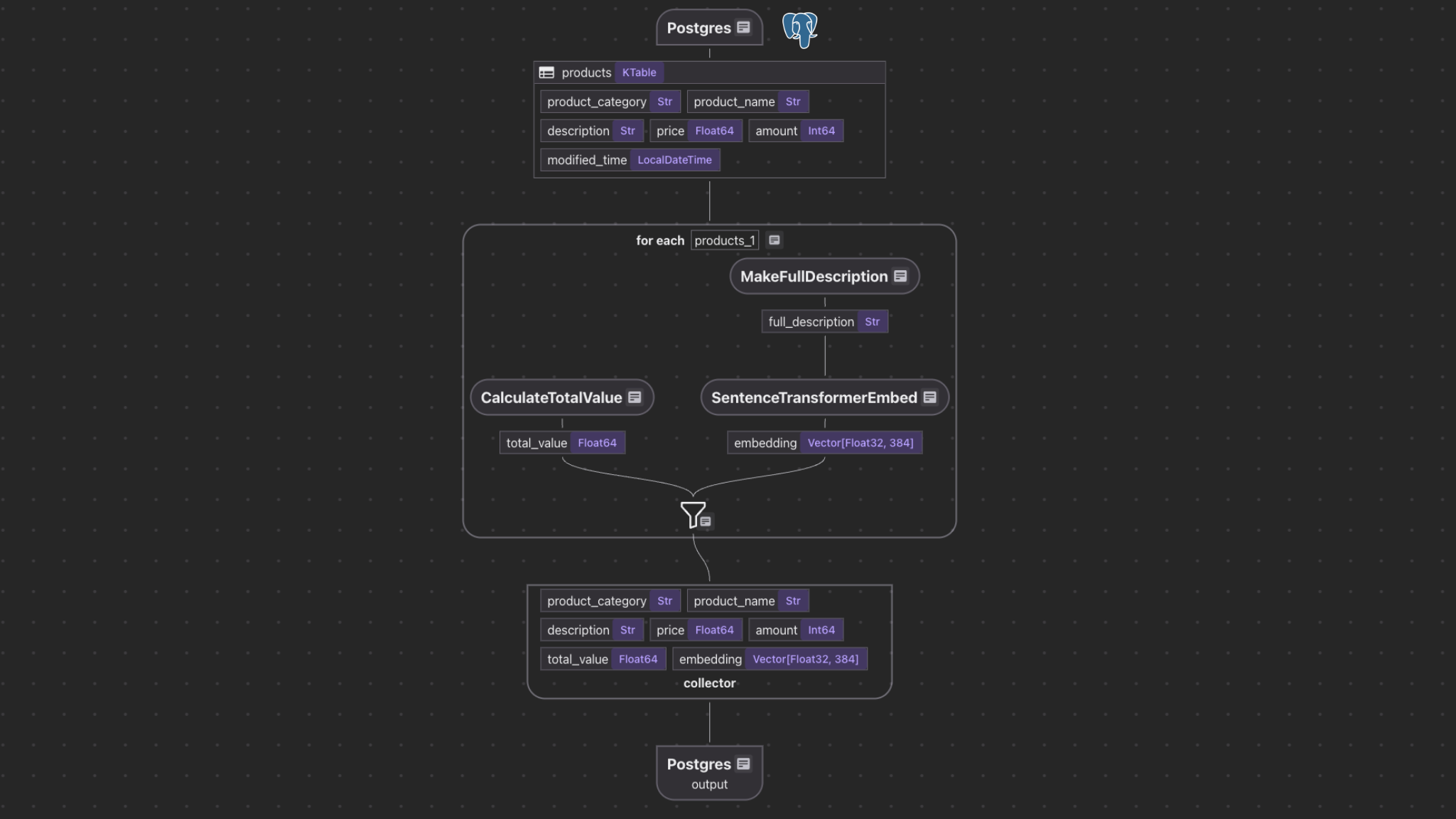
Our example demonstrates
- Reading data from a PostgreSQL table
source_products. - Computing additional fields (
total_value,full_description). - Generating embeddings for semantic search.
- Storing the results in another PostgreSQL table with a vector index using pgvector
This example is open sourced - examples/postgres_source.
Connect to source
flow_builder.add_source reads rows from source_products.
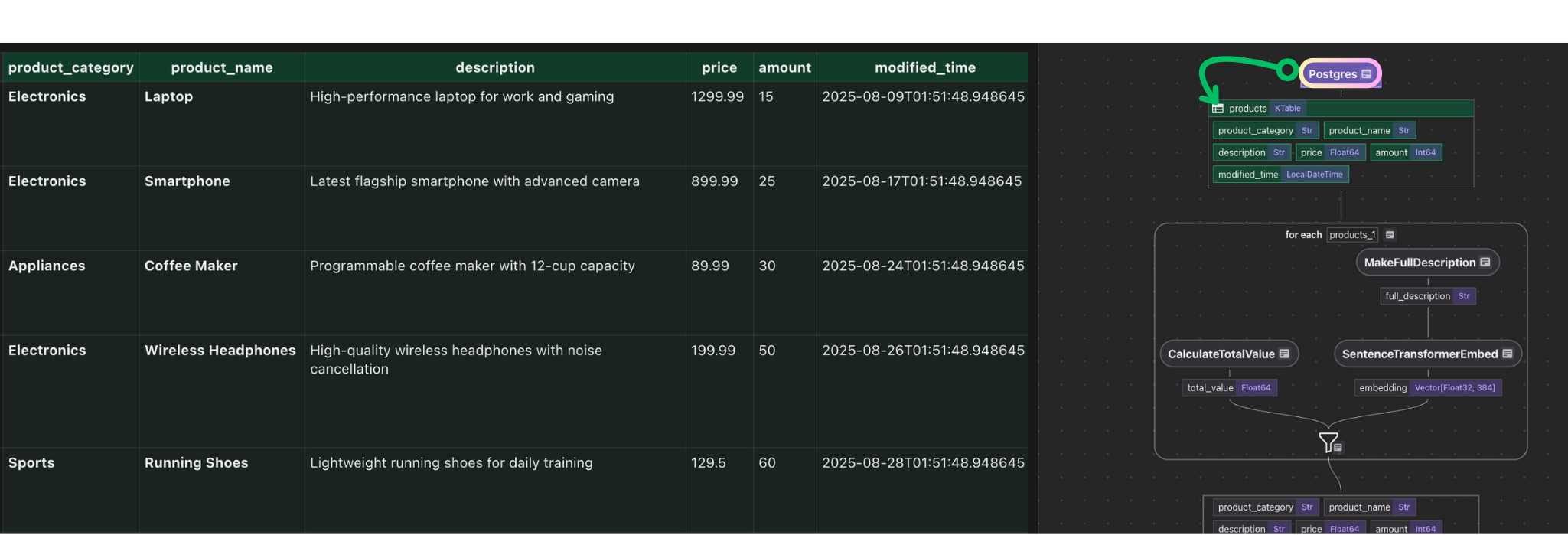
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="PostgresProductIndexing") def postgres_product_indexing_flow(flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope) -> None: data_scope["products"] = flow_builder.add_source( cocoindex.sources.Postgres( table_name="source_products", # Optional. Use the default CocoIndex database if not specified. database=cocoindex.add_transient_auth_entry( cocoindex.DatabaseConnectionSpec( url=os.environ["SOURCE_DATABASE_URL"], ) ), # Optional. ordinal_column="modified_time", notification=cocoindex.sources.PostgresNotification(), ), ) This step adds source data from PostgreSQL table source_products to the flow as a KTable.
\
- Incremental Sync: When new or updated rows are found, only those rows are run through the pipeline, so downstream indexes and search results reflect the latest data while unchanged rows are untouched.
ordinal_columnis recommended for change detection so the pipeline processes what's changed.notification: when present, enable change capture based on Postgres LISTEN/NOTIFY.
Check Postgres source for more details.
If you use the Postgres database hosted by Supabase, please click Connect on your project dashboard and find the URL there. Check DatabaseConnectionSpec for more details.
Simple Data Mapping / Transformation
Create a simple transformation to calculate the total price.
@cocoindex.op.function() def calculate_total_value(price: float, amount: int) -> float: """Compute total value for each product.""" return price * amount Plug into the flow:
with data_scope["products"].row() as product: # Compute total value product["total_value"] = flow_builder.transform( calculate_total_value, product["price"], product["amount"], ) 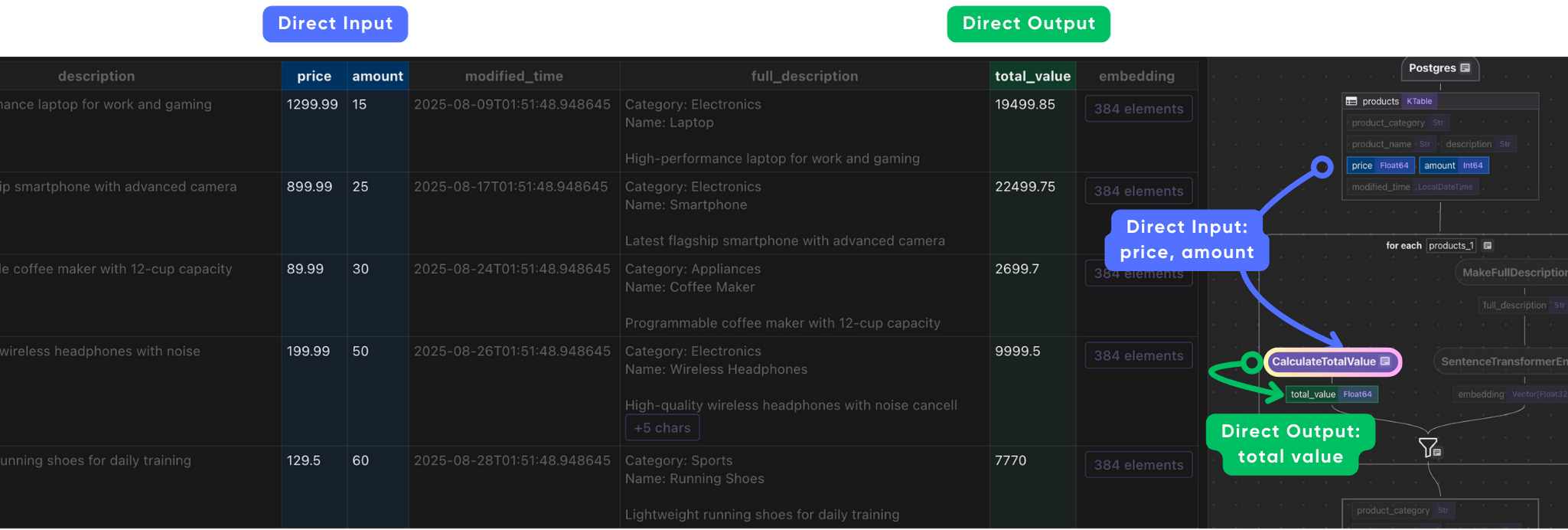
Data Transformation & AI Transformation
Create a custom function creates a full_description field by combining the product’s category, name, and description.
@cocoindex.op.function() def make_full_description(category: str, name: str, description: str) -> str: """Create a detailed product description for embedding." return f"Category: {category}\nName: {name}\n\n{description}" Embeddings often perform better with more context. By combining fields into a single text string, we ensure that the semantic meaning of the product is captured fully.
Now plug into the flow:
with data_scope["products"].row() as product: #.. other transformations # Compute full description product["full_description"] = flow_builder.transform( make_full_description, product["product_category"], product["product_name"], product["description"], ) # Generate embeddings product["embedding"] = product["full_description"].transform( cocoindex.functions.SentenceTransformerEmbed( model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2" ) ) # Collect data indexed_product.collect( product_category=product["product_category"], product_name=product["product_name"], description=product["description"], price=product["price"], amount=product["amount"], total_value=product["total_value"], embedding=product["embedding"], ) This takes each product row, and does the following:
-
builds a rich description.
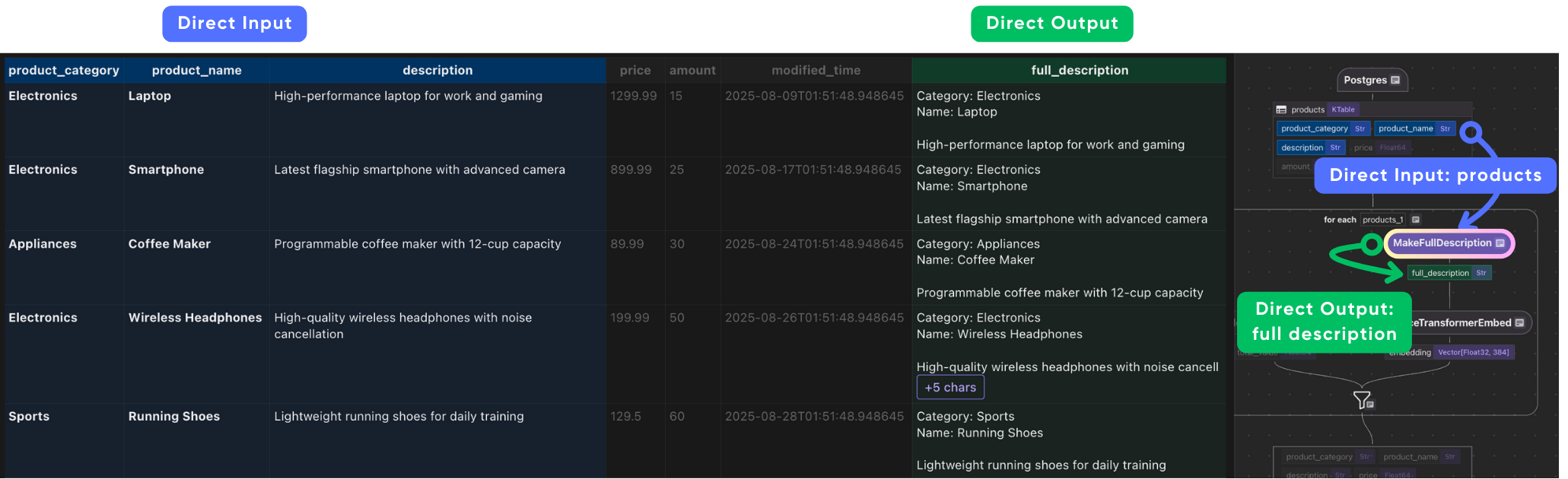
\
-
turns it into an embedding
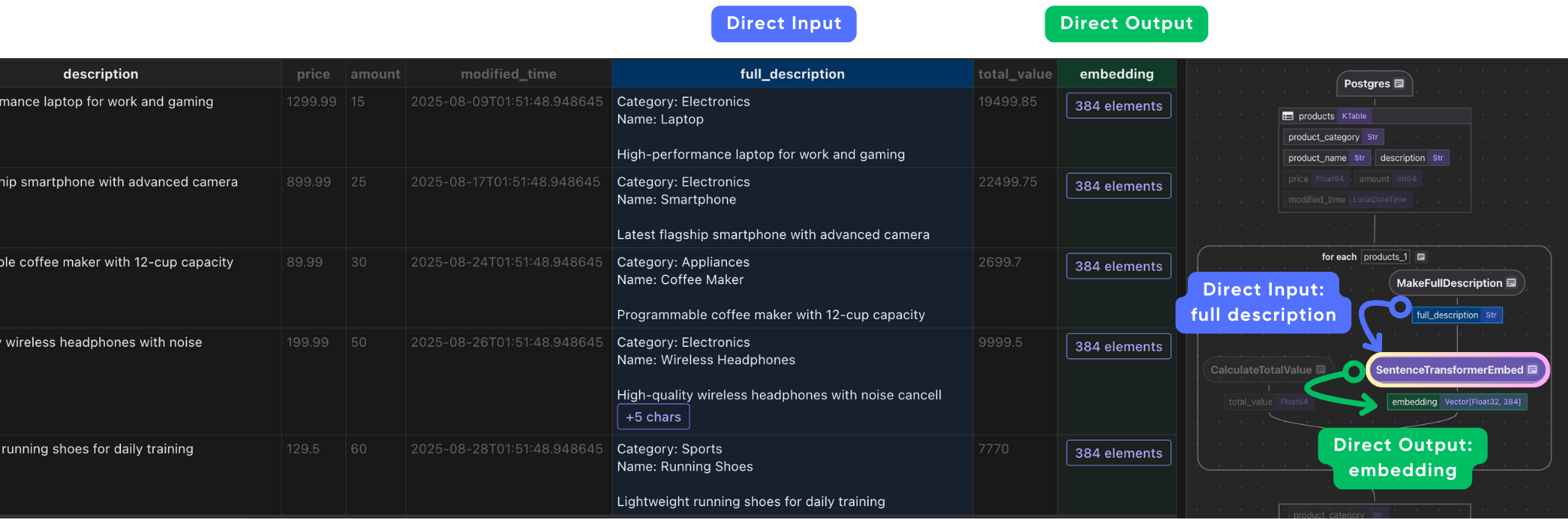
\
-
collects the embedding along with structured fields (category, name, price, etc.).
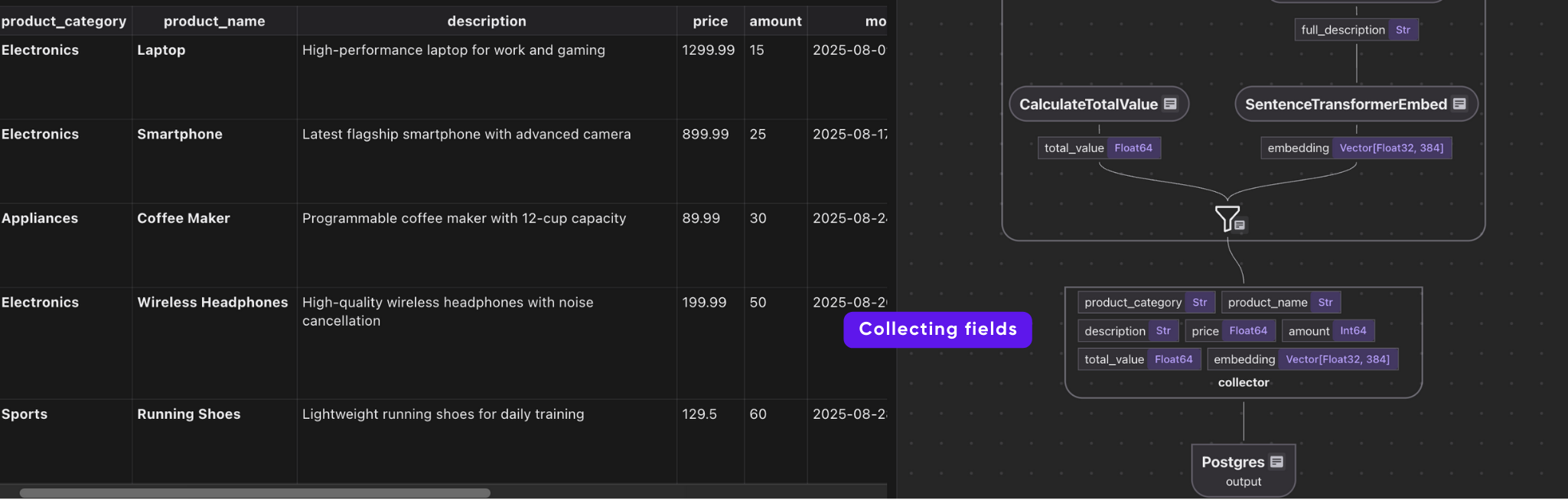
Export
indexed_product.export( "output", cocoindex.targets.Postgres(), primary_key_fields=["product_category", "product_name"], vector_indexes=[ cocoindex.VectorIndexDef( field_name="embedding", metric=cocoindex.VectorSimilarityMetric.COSINE_SIMILARITY, ) ], ) All transformed rows are collected and exported to a new PostgreSQL table with a vector index, ready for semantic search.
Field lineage
When the transform flow starts to getting complex, it's hard to understand how each field is derived. CocoIndex provides a way to visualize the lineage of each field, to make it easier to trace and troubleshoot field origins and downstream dependencies.
For example, the following image shows the lineage of the embedding field, you can click from the final output backward all the way to the source fields, step by step.
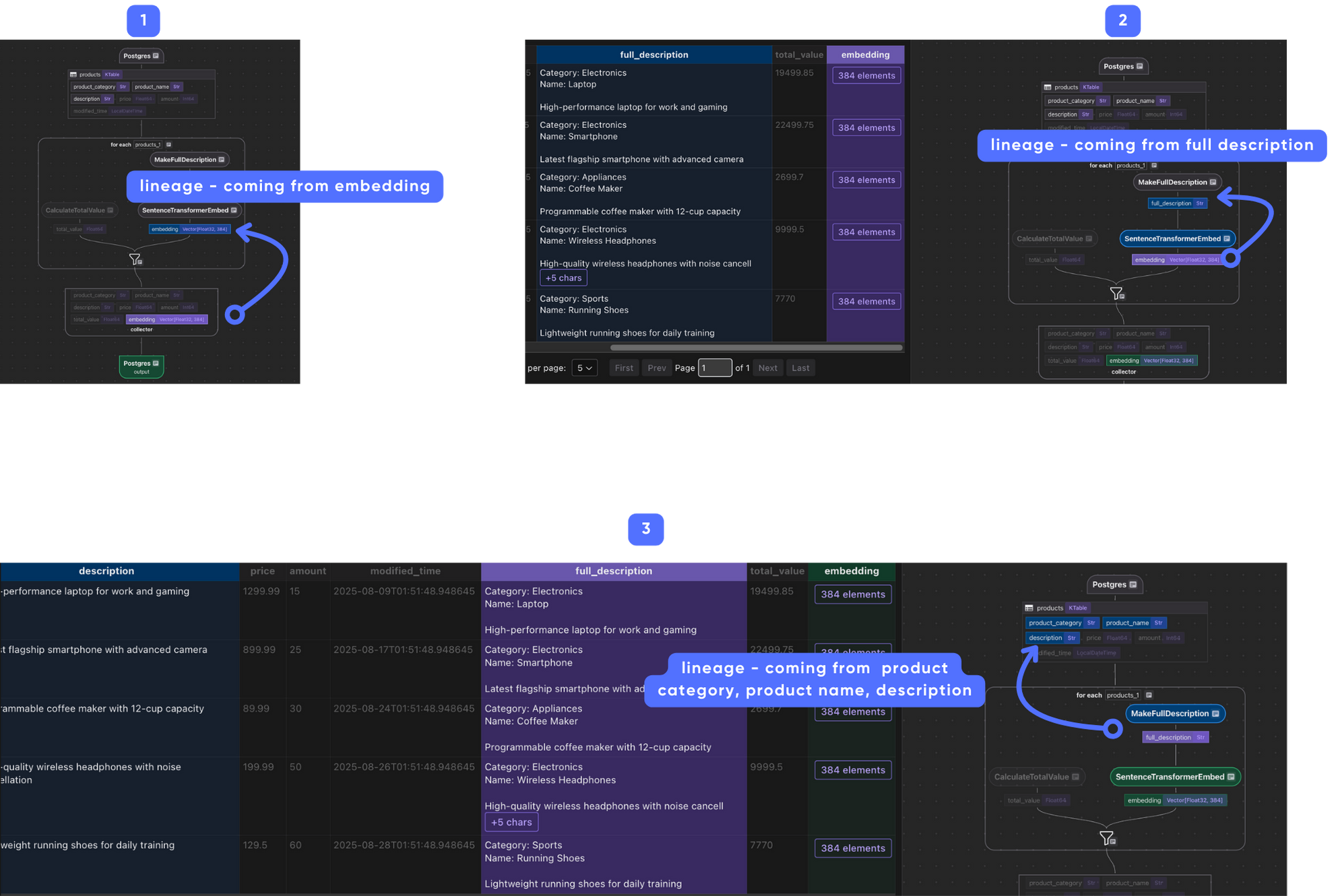
Running the Pipeline
- Set up dependencies:
pip install -e . - Create the source table with sample data:
psql "postgres://cocoindex:cocoindex@localhost/cocoindex" -f ./prepare_source_data.sql - Setup tables and update the index:
cocoindex update --setup main.py - Run CocoInsight:
cocoindex server -ci main You can walk through the project step by step in CocoInsight to see exactly how each field is constructed and what happens behind the scenes. It connects to your local CocoIndex server, with zero pipeline data retention.
Continuous Updating
For continuous updating when the source changes, add -L:
cocoindex server -ci -L main Check live updates for more details.
Search and Query the Index
Query
Runs a semantic similarity search over the indexed products table, returning the top matches for a given query.
def search(pool: ConnectionPool, query: str, top_k: int = 5) -> list[dict[str, Any]]: # Get the table name, for the export target in the text_embedding_flow above. table_name = cocoindex.utils.get_target_default_name( postgres_product_indexing_flow, "output" ) # Evaluate the transform flow defined above with the input query, to get the embedding. query_vector = text_to_embedding.eval(query) # Run the query and get the results. with pool.connection() as conn: register_vector(conn) with conn.cursor(row_factory=dict_row) as cur: cur.execute( f""" SELECT product_category, product_name, description, amount, total_value, (embedding <=> %s) AS distance FROM {table_name} ORDER BY distance ASC LIMIT %s """, (query_vector, top_k), ) return cur.fetchall() This function
- Converts the query text into an embedding (
query_vector). - Compares it with each product’s stored embedding (
embedding) using vector distance. - Returns the closest matches, including both metadata and the similarity score (
distance).
Create an command-line interactive loop
def _main() -> None: # Initialize the database connection pool. pool = ConnectionPool(os.environ["COCOINDEX_DATABASE_URL"]) # Run queries in a loop to demonstrate the query capabilities. while True: query = input("Enter search query (or Enter to quit): ") if query == "": break # Run the query function with the database connection pool and the query. results = search(pool, query) print("\nSearch results:") for result in results: score = 1.0 - result["distance"] print( f"[{score:.3f}] {result['product_category']} | {result['product_name']} | {result['amount']} | {result['total_value']}" ) print(f" {result['description']}") print("---") print() if __name__ == "__main__": load_dotenv() cocoindex.init() _main() Run as a Service
This example runs as a service using Fast API.
Summary
This approach unlocks powerful new possibilities for businesses to build fast and consistent semantic + structured search experiences, enabling advanced recommendations, knowledge discovery, and contextual analytics from hybrid data at scale.
With a single deployment, one lineage view, and a coherent mental model, CocoIndex is a future-ready framework that drives the next generation of data- and AI-powered applications with simplicity, rigor, and operational excellence.
Support Us
==We’re constantly adding more examples and improving our runtime. ⭐ Star CocoIndex on GitHub and share the love :heart:! And let us know what are you building with CocoIndex — we’d love to feature them.==
You May Also Like

Yarm Explained: Turning Trust and Tweets into Yield

Crossmint Partners with MoneyGram for USDC Remittances in Colombia
