Predicting Hard Drive Failures Using Mondrian Conformal Prediction
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Motivation and design goals
-
Related Work
-
Conformal prediction
4.1. Mondrian conformal prediction (MCP)
4.2. Evaluation metrics
-
Mondrian conformal prediction for Disk Scrubbing: our approach
5.1. System and Storage statistics
5.2. Which disk to scrub: Drive health predictor
5.3. When to scrub: Workload predictor
-
Experimental setting and 6.1. Open-source Baidu dataset
6.2. Experimental results
-
Discussion
7.1. Optimal scheduling aspect
7.2. Performance metrics and 7.3. Power saving from selective scrubbing
-
Conclusion and References
6. Experimental setting
In this section, we detail the dataset used for our study and the conducted experiments as well as their results.
6.1. Open-source Baidu dataset
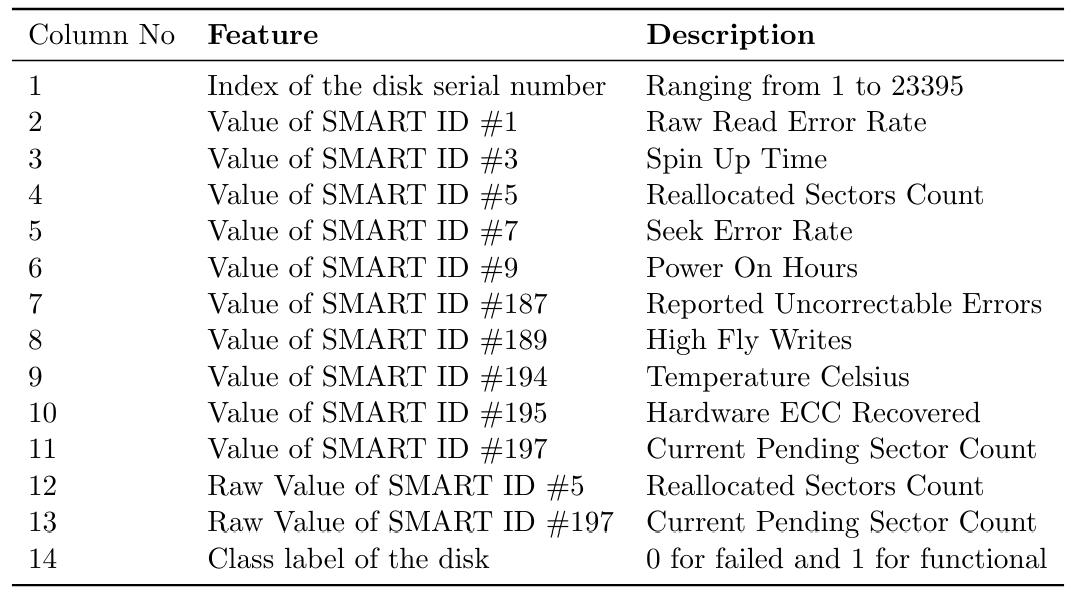
This dataset (DrTycoon, 2023) consists of samples collected from Seagate ST31000524NS enterprise-level HDDs, with a total of 23395 units and 13 features describing SMART attributes as shown in Table 2. The labeling of each disk was based on its operational status, categorized as either functional or failed. A significant proportion of disks, totaling 22962, were classified as functional, while a smaller subset of 433 was marked as failed, resulting in an imbalanced dataset. The SMART attribute values were recorded at an hourly interval for each disk, generating 168 samples per week for operational disks which gives 1,048,573 actual rows in the dataset corresponding to 23,395 disks (sampling frequency of 1 hour over a period of 2 years). The number of rows represents only the sample of operational disks that are provided in the dataset. However, the failed disks had varying numbers of samples, up to 20 days prior to failure.
\ 
\
6.2. Experimental results
For our experiments, we employed the Python programming language and used the MAPIE[3] library (map) for implementing Mondrian Conformal Prediction. The underlying algorithm employed in our experiments was the k Nearest Neighbors (kNN) algorithm.
\ The main goal of conducting the experimental evaluation is to showcase the significant reduction in the number of disk drives to be scrubbed that can be achieved by using the drive health predictor engine, i.e. exploiting the Mondrian conformal predictor.
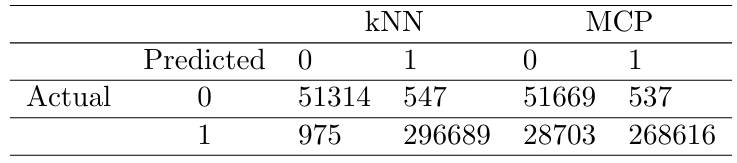
\ Table 3 shows a comparison between the confusion matrix for the drive disk classification problem using the underlying algorithm alone kNN and adding Mondrian Conformal Prediction, where label ”0” indicates a disk failure and label ”1” indicates a functional one. We can notice that, adding MCP, the number of disks correctly classified as failing has increased from 51314 to 51669, i.e., a difference of 355. This shows MCP helps to identify more disks of the minority class, but with a drawback that is a decrease in the number of disks correctly classified as healthy which has reduced from 296689 to 268616, i.e., a difference of 28073.
\ This issue can be solved by considering the confidence scores and their respective health status, as shown in Figure 5. There are nearly 126,224 drives with a health score greater than 99.95% for the disks labeled as healthy (left), out of total 349,525 disks, but when considering the relative health score, we categorize the 79,396 disk drives with a health score less than 99.9% as less healthy. Consequently, as shown in Table 4, we only select these 79,396 disk drives for scrubbing and skip the remaining 270,129. This approach significantly reduces the number of disks to be scrubbed to only 22.7%, resulting in lower power and energy consumption, which is noteworthy.
\ \ 
\ \ \ 
\ \
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs 4.0 International) license.
:::
[3] https://github.com/adamzenith/MAPIE/tree/Mondrian
:::info Authors:
(1) Rahul Vishwakarma, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (rahuldeo.vishwakarma01@student.csullb.edu);
(2) Jinha Hwang, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (jinha.hwang01@student.csulb.edu);
(3) Soundouss Messoudi, HEUDIASYC - UMR CNRS 7253, Universit´e de Technologie de Compiegne, 57 avenue de Landshut, 60203 Compiegne Cedex - France (soundouss.messoudi@hds.utc.fr);
(4) Ava Hedayatipour, California State University Long Beach, 1250 Bellflower Blvd, Long Beach, CA 90840, United States (ava.hedayatipour@csulb.edu).
:::
\
You May Also Like

Who’s Building the Next Phase of Artificial Intelligence? 20 Innovators Shaping the AI Industry in 2026

Will XRP Price Increase In September 2025?
