Google Launches GCUL: A New Blockchain Built for Banks and Financial Institutions

Google Cloud has officially entered the blockchain infrastructure race with its new Layer 1 network called the Google Cloud Universal Ledger (GCUL).
Unlike most blockchain networks that use complex programming languages, GCUL runs on Python-based smart contracts. This makes it easier for traditional finance developers to build applications without learning new coding languages.
What Makes GCUL Different
GCUL operates as a private and permissioned network, meaning only approved institutions can access it. This design focuses on compliance and regulatory requirements that banks need to follow.
Rich Widmann, Google’s head of Web3 strategy, explained the platform’s neutral approach in a recent LinkedIn post. “Tether won’t use Circle’s blockchain – and Adyen probably won’t use Stripe’s blockchain. But any financial institution can build with GCUL,” he wrote.
Source: @rich_widmann
The platform offers several key features that set it apart from other blockchain networks:
- Single API access for easy integration
- Built-in compliance tools including KYC checks
- 24/7 capital markets infrastructure
- Support for commercial bank money on-chain
- Stable billing model without volatile gas fees
CME Group Partnership Shows Real-World Testing
Google’s partnership with CME Group, one of the world’s largest derivatives exchanges, provides concrete evidence of GCUL’s development. CME completed the first phase of integration and testing in March 2025.
Terry Duffy, CME Group Chairman and CEO, said the technology “has the potential to deliver significant efficiencies for collateral, margin, settlement and fee payments as the world moves toward 24/7 trading.”
The companies plan to begin broader testing with market participants later in 2025. Full commercial services are expected to launch in 2026.
Competition Heats Up in Corporate Blockchain Space
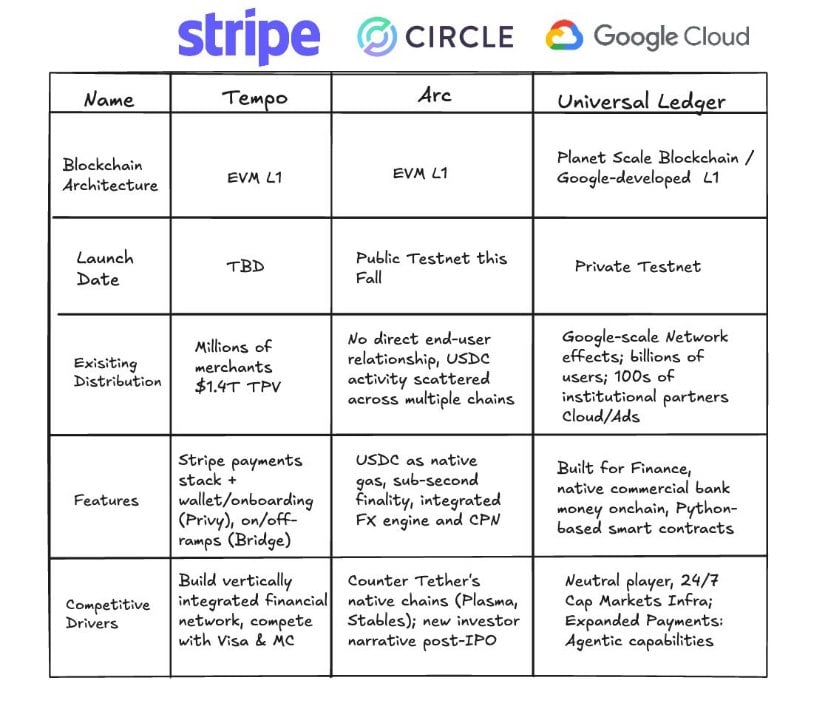
GCUL enters a competitive market where major tech companies are building their own blockchain networks. Stripe is developing Tempo, an Ethereum-compatible blockchain focused on merchant payments. Circle is creating Arc, which centers around its USDC stablecoin.

Source: cloud.google
Each platform takes a different approach:
- Stripe’s Tempo: Focuses on extending existing merchant payment systems into blockchain
- Circle’s Arc: Uses USDC as the native token with emphasis on foreign exchange
- Google’s GCUL: Aims to be neutral infrastructure that any institution can use
The timing reflects growing demand in the payments industry. Stablecoin volumes tripled in 2024, reaching $5 trillion in organic transactions globally.
Python Programming Creates Developer Advantage
GCUL’s use of Python for smart contracts represents a strategic choice. Most blockchain networks require developers to learn specialized languages like Solidity (Ethereum) or Rust (Solana).
Python is already widely used in finance, data analysis, and machine learning. This familiarity could speed up adoption among traditional financial institutions that want to explore blockchain technology.
The platform currently runs on a private testnet with selected partners. Google plans to release more technical details in the coming months as development progresses toward commercial deployment.
Questions About Neutrality and Control
Despite Google’s claims of neutrality, some industry experts question whether the company can remain impartial. Google operates extensive business interests in payments, cloud services, and advertising that could create conflicts.
Dr. Sean Yang, chief technology officer at OORT, told Decrypt that Google’s neutrality claim may be “more marketing than reality” given the company’s “massive conflicts of interest.”
The blockchain infrastructure market continues to grow as institutions seek alternatives to traditional payment rails. Google’s entry adds another major player to a space that includes established networks like Ethereum and newer institutional-focused platforms.
Google has not confirmed whether GCUL will eventually become more open or remain a closed system. The company indicated it might expand access “as regulations evolve.”
Market Impact Expected
The platform targets several key use cases that financial institutions need:
- Cross-border payments and settlements
- Asset tokenization
- Collateral and margin management
- Wholesale payment processing
Google’s existing relationships with cloud infrastructure customers could provide a distribution advantage. The company serves billions of users and hundreds of institutional partners through its cloud platform.
The success of GCUL will likely depend on whether financial institutions trust Google to maintain neutral operations and competitive pricing compared to existing blockchain solutions.
The Road Ahead
GCUL represents Google’s most direct entry into blockchain infrastructure for financial services. The platform’s Python-based approach and focus on compliance could appeal to traditional banks that have been cautious about blockchain adoption.
The 2026 commercial launch timeline gives Google time to refine the technology and build partnerships with additional financial institutions beyond CME Group. Success will depend on demonstrating real cost savings and efficiency improvements compared to current payment systems.
With major tech companies now competing to build the infrastructure for digital finance, the stakes are high for who controls the backbone of future payment systems.
You May Also Like

X to cut off InfoFi crypto projects from accessing its API

X Just Killed Kaito and InfoFi Crypto, Several Tokens Crash
