Zero Trust Network Access(ZTNA) Enforcement Using Real Time Risk Scoring & Dynamic Path Segmentation
\ As organizations rapidly embrace cloud services, remote work, and distributed architectures, traditional perimeter-based security has become obsolete. Today’s users, devices, and applications operate far beyond corporate network boundaries—rendering legacy security models ineffective against modern threats.
According to Gartner, by 2025, 60% of enterprises will phase out most of their remote access VPNs in favor of ZTNA. Meanwhile, IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report shows that organizations with Zero Trust deployed saved an average of $1.76 million per breach.
As threats grow more dynamic and sophisticated, ZTNA itself must evolve. The next phase of Zero Trust requires access decisions that adapt in real time—driven by continuous risk assessment and enforced through dynamic path segmentation.
Why Traditional ZTNA Needs Real-Time Adaptability?
Traditional ZTNA models authenticate users and validate device posture before granting access. But after authentication, most policies remain static—unable to respond to changes in user behavior, device compromise, or emerging threats during an active session. This exposes organizations to risks that appear after access is granted.
For example, a device may become infected mid-session, or a trusted user may begin accessing unusual resources. Static controls simply cannot detect these shifts.
Real-World Example: The SolarWinds Lesson
The 2020 SolarWinds attack demonstrated exactly why static access decisions fail. Attackers compromised legitimate credentials and moved laterally through networks for months all while appearing as trusted users.
A dynamic, risk-aware ZTNA system would have:
- Flagged anomalous behavior
- Triggered step-up authentication
- Restricted or revoked access
before substantial damage occurred.
Where Static ZTNA Fails: Specific Scenarios
- Credential theft \n A user’s credentials are stolen via phishing, but their device and session remain trusted.
- Insider threat \n An authenticated employee begins accessing unusual resources.
- Session hijacking \n An attacker takes over a valid authenticated session.
- Device compromise \n Malware infects a previously compliant device mid-session.
Static ZTNA cannot respond to any of these threats once initial access is granted.
Real-Time Risk Scoring: The Engine of Adaptive Access
Real-time risk scoring adds a continuous evaluation layer that monitors user and device trustworthiness throughout an active session. Instead of relying on a one-time identity check, the system calculates a composite, evolving risk score based on:
Key Risk Inputs
- User behavior: Login anomalies, activity deviations, unusual access patterns
- Device posture: OS version, patch level, security configuration, EDR signals
- Environmental signals: Geolocation, connection source, network reputation
- Threat intelligence: Known malicious IPs, IOCs, active attack campaigns
With continuous scoring, ZTNA can dynamically adjust permissions:
- Low risk → seamless access
- Medium risk → step-up authentication or restricted access
- High risk → session termination or quarantine
This ensures that access privileges always reflect the current threat landscape, not outdated assumptions.
Dynamic Path Segmentation: Reimagining Secure Connectivity
Dynamic path segmentation complements real-time risk scoring by enforcing least-privilege network access at the transport level. Unlike VPNs which provide broad network exposure once authenticated—dynamic segmentation creates per-application secure pathways that exist only as long as trust conditions remain valid.
These microtunnels:
- Are built using software-defined routing
- Exist only for individual applications
- Offer zero lateral movement
- Automatically adjust or terminate based on risk changes
How Dynamic Path Segmentation Works?
\ ** 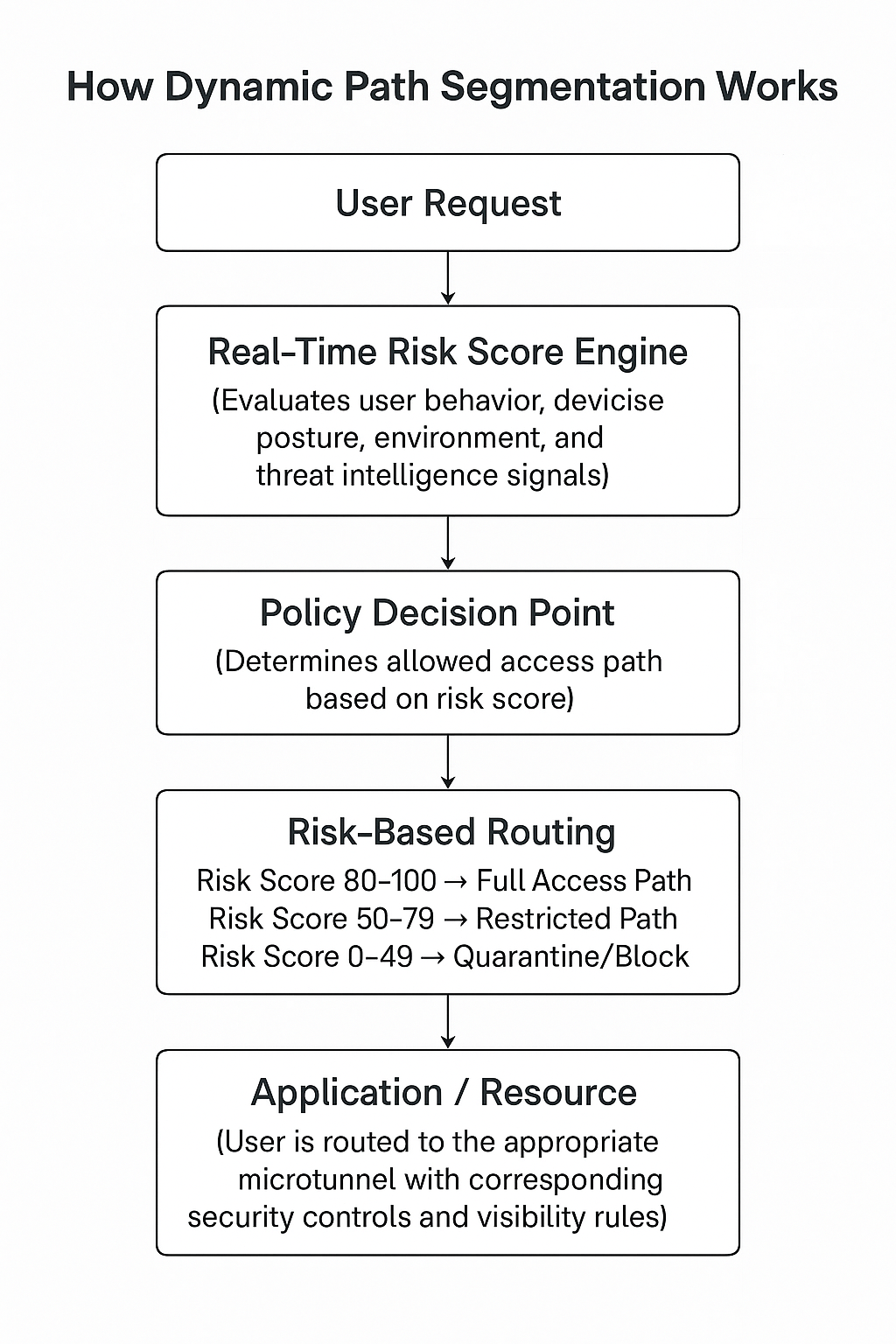 **
**
\ Each routing path corresponds to a dedicated network segment with unique security controls, logging levels, and permissions.
ZTNA + Real-Time Risk Scoring + Dynamic Path Segmentation: A Unified Adaptive Model
Together, these three components create an intelligent, self-adjusting Zero Trust architecture.
How the Unified Model Operates
- Real-time access decisions: Authentication adapts based on the current risk score
- Continuous monitoring: Risk scores evolve with each user action
- Network-level enforcement: Path segmentation isolates users based on trust
- Feedback loop: Logged events improve future detection accuracy
Access always reflects least privilege, and threats are contained before lateral movement occurs.
Implementation Considerations
When rolling out this unified model, organizations should consider:
- Start with visibility \n Deploy risk scoring in monitoring mode to baseline behaviors.
- Phased enforcement \n Introduce step-up authentication first before enabling automated blocking.
- Integration requirements \n Connect SIEM, identity provider, and endpoint tools to feed risk signals.
- False positive tuning \n Overly aggressive thresholds create friction—tune gradually.
- Compliance alignment \n Map risk thresholds to regulatory frameworks (PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2).
Key Integration Points
- Identity Provider (IdP): User identity & posture
- EDR: Device health and threat signals
- SIEM/SOAR: Threat intelligence correlation
- CASB: Application visibility and governance
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
1. Over-Aggressive Risk Thresholds \n Problem: Excessive false positives frustrate users. \n Solution: Start permissively in monitoring mode and tighten gradually.
2. Insufficient Signal Sources
Problem: Limited visibility results in inaccurate scoring. \n Solution: Integrate multiple data streams for holistic assessment.
3. Ignoring User Experience
Problem: High friction drives users to insecure workarounds. \n Solution: Optimize for low-risk common cases; add friction only when needed.
4. Static Policies on Dynamic Systems
Problem: Treating risk scoring as set-and-forget. \n Solution: Review thresholds and detection patterns regularly.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Network Access has become a foundational element of modern cybersecurity, but its effectiveness depends heavily on its ability to evolve alongside the shifting threat landscape. Traditional, static ZTNA models while valuable are no longer sufficient in an environment where user behavior, device posture, and external threat conditions can change at any moment. By integrating real-time risk scoring and dynamic path segmentation, organizations can elevate ZTNA from a one-time gatekeeper into a continuously adaptive security framework. This dynamic approach ensures that trust is never assumed and that access decisions reflect current conditions rather than outdated assumptions made at login.
The combination of continuous risk assessment and flexible, per-application segmentation dramatically reduces the chances of lateral movement, session compromise, or unnoticed insider threats. This unified model provides security teams with unprecedented visibility and responsiveness, enabling them to contain risks before they escalate into breaches. At the same time, it improves user experience by removing unnecessary friction for trusted interactions and only introducing additional checks when warranted by risk signals.
Looking forward, the future of adaptive ZTNA will be shaped by advances in AI, predictive analytics, and cross-organization threat intelligence. As these technologies mature, organizations will gain the ability to anticipate risks rather than simply react to them. Those who adopt adaptive ZTNA today will be better equipped to handle the increasingly sophisticated threats of tomorrow, strengthening both operational resilience and user trust.
For organizations ready to take their next step, the path forward begins with assessing current access controls, identifying risk signal gaps, and piloting real-time scoring in a targeted environment. With thoughtful implementation and ongoing refinement, adaptive ZTNA becomes not just a security enhancement, but a transformative shift in how access is governed across the enterprise.
\
:::tip This story was distributed as a release by Sanya Kapoor under HackerNoon’s Business Blogging Program.
:::
\
You May Also Like

Pi Network Pi Day Preview: Major Product Updates and Real World Expansion Ahead

Fed Decides On Interest Rates Today—Here’s What To Watch For

The DeFi Evolution on Pi Network: Building Utility and Global Integration
The DeFi Evolution on Pi Network: Building Utility and Global Integration
Decentralized finance, or DeFi,