LUCAS one way attack drone (with inert warhead) at Yuma Proving Ground
U.S. Army
Last week United Stated Central Command (CENTCOM) announced Task Force Scorpion Strike (TFSS), and that a squadron had already been formed, “the U.S. military’s first one-way-attack drone squadron,” based in the Middle East. The release includes images of the unit’s Low-cost Unmanned Combat Attack System (LUCAS) drones, reverse-engineered from Shaheds used by Iran and Russia.
The announcement comes just four months after Pete Hegseth ordered an acceleration of the acquisition and fielding of affordable drone technology. The location in Iran’s back yard is hardly coincidental. Previously the U.S. could only launch small numbers of expensive legacy missiles. Now Scorpion Strike can unleash the sort of massive drone barrages that Russia regularly launches and “flip the script on Iran” as one U.S. official puts it.
Or can it? Other information suggests LUCAS is far from ready for action.
*Warhead Not Included?
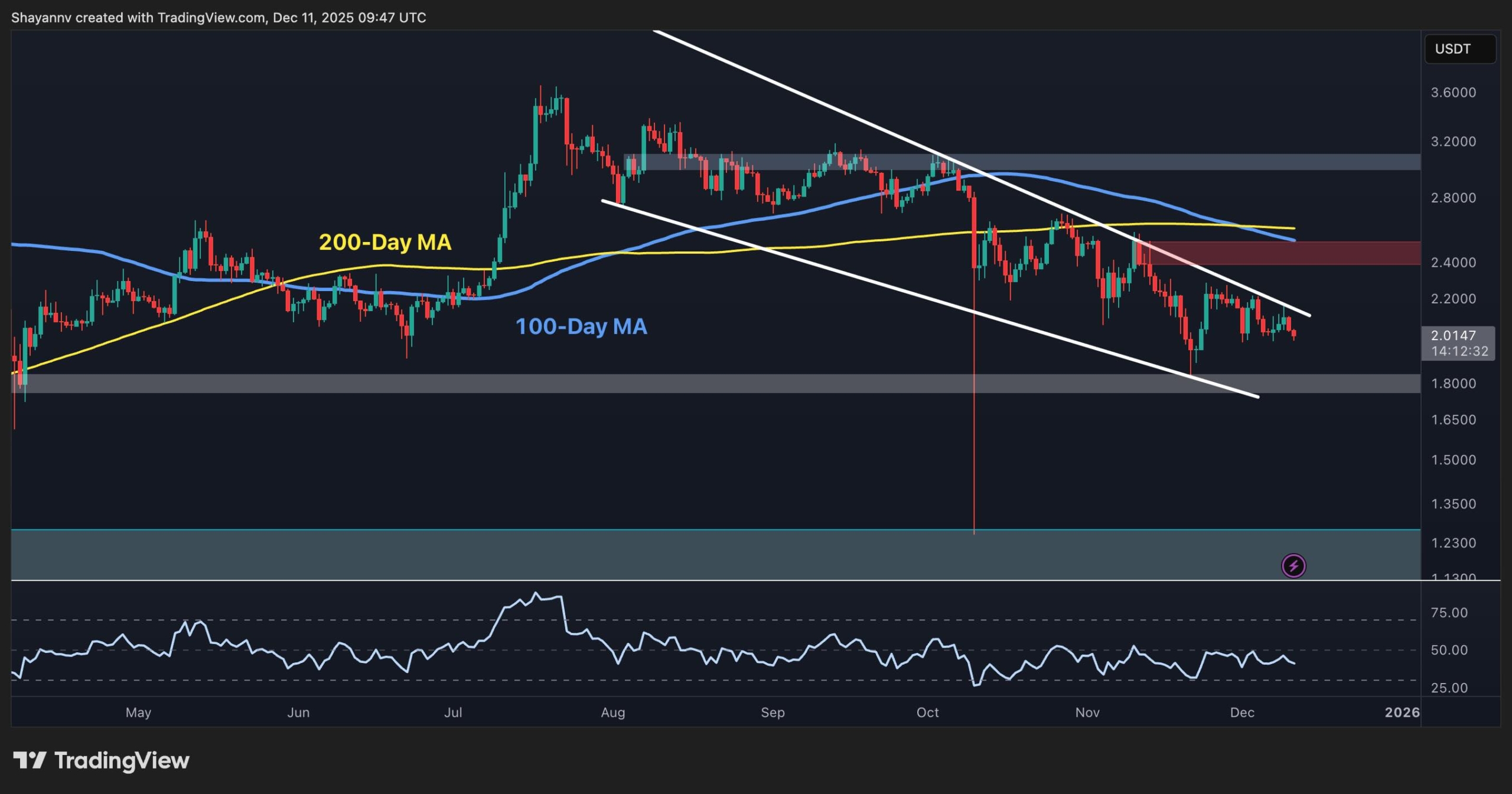
The U.S. Army also issued a press release last week, describing the testing of LUCAS at the Yuma Proving Ground (YPG). The image with the release shows a craft which looks identical to those displayed by CENTCOM.
Scorpion Strike’s LUCAS drones
CENTCOM
YPG includes over 2,000 miles of restricted airspace in the desert, making it the ideal place to test long range systems. But there is no testing with live weapons yet.
“We’re getting our baby steps in before we conduct safety certification testing,” states Col. Nicholas Law, Director of Experimentation in the Office of the Under Secretary of War for Research & Engineering, in the release.
But it seems the warheads for the drones have not been made.
“The warhead that will eventually be integrated into LUCAS isn’t constructed yet, but it will also be low-cost and mass produced by multiple manufacturers. Evaluators are currently testing LUCAS with inert payloads,” states the release. (My emphasis)
In other words, these are drones with dummy warheads. So while the CENTCOM release says that they have deployed LUCAS drones, it seems that the drones shown are for display purposes only and that Scorpion Strike force is ways from being able to make strikes.
The original Iranian Shahed-136
Wikimedia commons
It is possible that there is some kind of stopgap warhead in place for Scorpion Strike; the Ukrainians and Russians do this kind of improvisation all the time (for example, the Flamingo cruise missile warhead is a repurposed FAB-1000 aircraft bomb). But without an urgent requirement it is hard to see why such a duplication of effort would be carried out.
How Much Bang For Your Buck?
The current LUCAS model looks like the FLM-136 made by SpektreWorks, described as a close copy of the Iranian Shahed series and marketed as a reliable, cost-effective threat emulator. However, Business Insider noted that a similar drone displayed in the Pentagon Courtyard was described as FLM-131 rather than FLM-136.
Pete Hegseth at a display of U.S. made low-cost drones at the Pentagon in July
U.S> Department of War
This suggests that LUCAS is not a copy of the Shahed-136 which the Russians rebranded as Geran-2, but its little brother, the Shahed-131 or Geran-1. These are rarely seen in Ukraine, where the larger 136 completely dominates.
The FLM-136 specifications suggest something morelike the 131. The 131 has a range of around 500 miles compared to more than 1,000 miles for the 136; and the 131 carries a 40-pound warhead compared to an almost-200 pound warhead on the 136. According to SpektreWorks data sheet, the FLM-136 has a range of at least 400 miles and carries a 40-pound payload like the Shahed-131, making it a closer match with the smaller version.
It is also possible that the LUCAS/FLM-131 is a separate project and carries an even smaller warhead than the FLM-136. In any case, it looks like the U.S. drones will strike with a fraction of the power of their Iranian and Russian counterparts.
Numbers Game: How Many LUCAS?
As Law notes, the point of LUCAS is to make large numbers of drones.
“We want to produce a lot of these in a rapid fashion,” states Law. “It’s not a single manufacturer: it’s designed to go to multiple manufacturers to be built in mass quantities.”
In large numbers, LUCAS can swamp and deplete defenses, strike large numbers of targets, or maintain a series of attacks over a prolonged period. These are all things which are impossible with a handful of cruise missiles, but which are part of the part of the war in Ukraine.
LUCAS drones shown in the CENTCOM Scorpion Strike release
CENTCOM
According to an official interview by TWZ, LUCAS drones cost $35,000 each, a close match with the “$35,000, $40,000” figure mentioned by Donald Trump as the cost of Russian attack drones, quoted at the Pentagon presentation in July.
Neither CENTCOM nor the US Army say how many LUCAS will be procured.
There is a contract to SpektreWorks from U.S. Army Contracting Command which kicked off on 24th July 2025 – the week after the Pentagon display – and runs to 31/12/2025 for “FLM-131 LUCAS FOLLOW-ON PRODUCTION.” This shows a total of $30m obligated. (Note FLM-131, not 136)
If we assume that all of that $30m goes on LUCAS drones, and that none of it will be absorbed by support equipment such as launch catapults, ground control stations, communications, spares and training – then at $35 k per unit the contract would yield around 850 drones.
However, as TWZ note, the LUCAS drones shown by CENTCOM seem to be of two types. Some are the basic, vanilla version which likely relies on satellite guidance, others have a nose camera and satellite communication link, indicating that they may be controlled by a human operator. These correspond to Russian developments which have evolved from the original Iranian design. The more advanced versions may have a higher price tag than the basic $35k and numbers may be lower.
850 drones is a pretty good start, especially when you consider that the Navy is only buying 40 Tomahawk cruise missiles next year.
The Department of War insists on X that “Drone dominance isn’t coming. It’s here.”
But the Russians launched more than 5,400 Shahed-type drones last month alone, and whose production is steadily rising. At a conservative estimate the Russians are outpacing the U.S. by a factor of ten.
The Russian drones are battle-proven, and they have warheads – many types, including high explosive/fragmentation, thermobaric warheads for demolishing buildings, and a napalm-type liquid incendiary. Some even carry ‘extras’ in addition to the warhead, scattering cluster bomblets or anti-tank mines along their path. This destructive power is possible because of the Shahed’s capacity for a heavy payload which the LUCAS lacks.
The Need For Mass
President Zelensky with one of the thousands of Shaheds launched by Russia each month
Office of the President of Ukraine
Back in July we asked whether the purpose of LUCAS was to be seen to be meeting a Presidential demand: he called for $35,000 attack drones, so he got $35,000 attack drones. But Scorpion Strike Force needs to be more than a token unit for press releases.
Announcing deployment in the Middle East looks premature given that the testing at Yuma is still ongoing. And the enthusiasm for large numbers of low-cost drones to match the capabilities of potential adversaries represents a huge and important shift. But it needs to be backed with mass.
SThe Pentagon is putting a billion dollars into attack drones, and similar sums need to be invested in capabilities like LUCAS. The U.S. needs plenty of low-cost attack drones—with warheads.
Source: https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidhambling/2025/12/09/us-deploys-scorpion-strike-drones–but-do-they-have-warheads/