MIVPG: Multi-Instance Visual Prompt Generator for MLLMs
\
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Learning
2.2. Multiple Instance Learning
-
Methodology
3.1. Preliminaries and Notations
3.2. Relations between Attention-based VPG and MIL
3.3. MIVPG for Multiple Visual Inputs
3.4. Unveiling Instance Correlation in MIVPG for Enhanced Multi-instance Scenarios
-
Experiments and 4.1. General Setup
4.2. Scenario 1: Samples with Single Image
4.3. Scenario 2: Samples with Multiple Images, with Each Image as a General Embedding
4.4. Scenario 3: Samples with Multiple Images, with Each Image Having Multiple Patches to be Considered and 4.5. Case Study
-
Conclusion and References
\ Supplementary Material
A. Detailed Architecture of QFormer
B. Proof of Proposition
C. More Experiments
Abstract
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved SOTA performance in various visual language tasks by fusing the visual representations with LLMs leveraging some visual adapters. In this paper, we first establish that adapters using query-based Transformers such as Q-former is a simplified Multi-instance Learning method without considering instance heterogeneity/correlation. We then propose a general component termed Multi-instance Visual Prompt Generator (MIVPG) to incorporate enriched visual representations into LLMs by taking advantage of instance correlation between images or patches for the same sample. Quantatitive evaluation on three public vision-language (VL) datasets from different scenarios shows that the proposed MIVPG improves Q-former in main VL tasks.
1. Introduction
In recent years, with the disruptive changes brought to the Machine Learning community by Large Language Models (LLMs)[4, 29–31], an increasing number of researchers have been exploring the application of LLMs in the realm of multimodality, giving rise to Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs)[2, 21, 22, 24, 48]. One of the most common forms of multimodality involves the combination of images and text. Just as humans excel in using both images and text to perform tasks, the fusion of images and text in multimodal applications finds wide real-world use, such as in Image Captioning[13, 32, 43, 44] and Visual Question Answering (VQA)[3, 11, 25, 38]. Leveraging the formidable generalization capabilities of large models, MLLMs have achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in various few-shot and fine-tuning tasks.
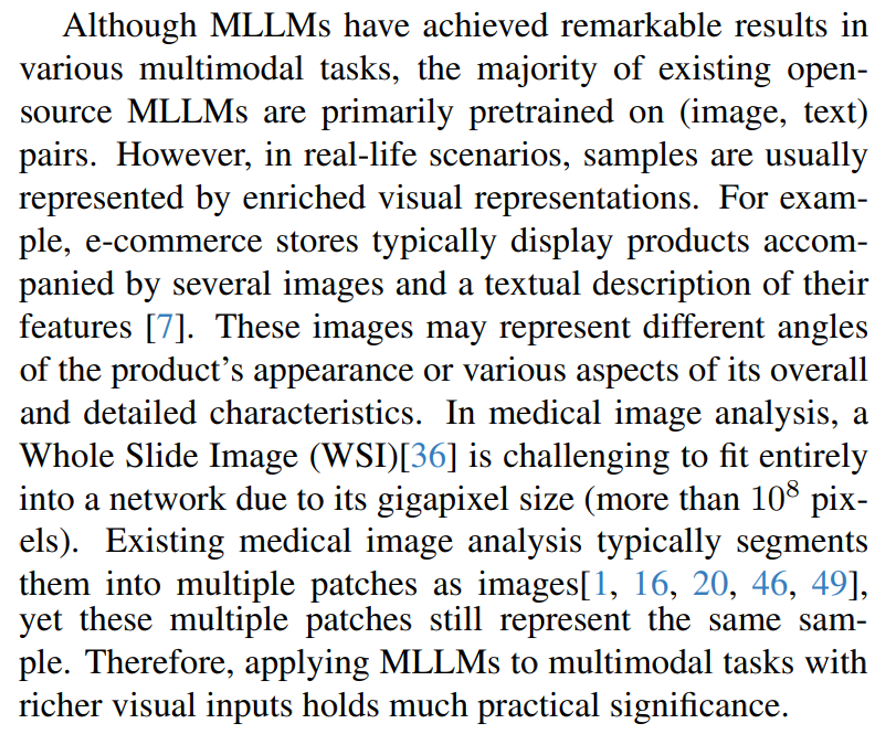
\ ![Figure 1. Left: Exemplary images from [7], portraying ecommerce products captured from various aspects. Right: Illustration of a Whole Slide Image (WSI) sourced from [36]. Each WSI is composed of multiple patches, exhibiting dimensions comparable to those of natural images.](https://cdn.hackernoon.com/images/fWZa4tUiBGemnqQfBGgCPf9594N2-pb033wu.png)
\ 
\ In contemporary MLLMs, the integration of images is achieved through a critical component for imparting visual understanding to LLMs through transforming images to visual tokens, which we termed Visual Prompt Generators (VPGs) in this paper. SOTA MLLMs, such as BLIP2[22], Flamingo[2], and MiniGPT-4[48], utilize attention-based VPGs with learnable query embeddings. These embeddings engage in cross-attention with visual embeddings, extracting visual information for LLM input. In this work, we introduce a novel approach, the Multi-instance Visual Prompt Generator (MIVPG), designed to handle diverse visual inputs. Drawing inspiration from Multiple Instance Learning (MIL), MIVPG treats images or patches of a sample as a set of instances, forming a ”bag.” Unlike traditional machine learning tasks, MIL performs predictions at the bag level rather than the instance level, employing permutationinvariant functions to aggregate instances. MIVPG extends this concept by considering correlations and relationships across visual representations, facilitating signal pooling from different dimensions. Additionally, we establish that the commonly used QFormer[22, 48] is a limited MIL module, prompting the introduction of MIVPG. We showcase MIVPG’s enhanced performance across three distinct scenarios, including common natural images, gigapixelsized pathological images, and e-commerce products with multiple images.
\ In summary, our contributions in this paper can be outlined as follows:
\ • We introduce a general and flexible component MIVPG to incorporate enriched visual representations and their relationship into the open source LLM.
\ • We establish that the commonly used QFormer is a simplified case of MIVPG with limited capability and conduct experiments to show the superiority of our component over the QFormer.
\ • We evaluate the MIVPG on three public datasets from distinct scenarios and showcase that the MIVPG supports visual representation aggregation from different dimensions: image dimension for e-commerce data and patch dimension for WSI. MIVPG outperforms the QFormer by a significant margin in all datasets, which demonstrates the effectiveness and generalizability of the proposed component.
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Wenliang Zhong, The University of Texas at Arlington (wxz9204@mavs.uta.edu);
(2) Wenyi Wu, Amazon (wenyiwu@amazon.com);
(3) Qi Li, Amazon (qlimz@amazon.com);
(4) Rob Barton, Amazon (rab@amazon.com);
(5) Boxin Du, Amazon (boxin@amazon.com);
(6) Shioulin Sam, Amazon (shioulin@amazon.com);
(7) Karim Bouyarmane, Amazon (bouykari@amazon.com);
(8) Ismail Tutar, Amazon (ismailt@amazon.com);
(9) Junzhou Huang, The University of Texas at Arlington (jzhuang@uta.edu).
:::
\
You May Also Like

Hyperliquid Strategies Inc. announces a $30M stock buyback program
Ethereum Price Prediction: ETH Targets $10,000 In 2026 But Layer Brett Could Reach $1 From $0.0058
